 |
CMSIS-RTOS2
Version 2.1.0
Real-Time Operating System: API and RTX Reference Implementation
|
 |
CMSIS-RTOS2
Version 2.1.0
Real-Time Operating System: API and RTX Reference Implementation
|
Synchronize threads using event flags. More...
Data Structures | |
| struct | osEventFlagsAttr_t |
| Attributes structure for event flags. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef void * | osEventFlagsId_t |
Functions | |
| osEventFlagsId_t | osEventFlagsNew (const osEventFlagsAttr_t *attr) |
| Create and Initialize an Event Flags object. More... | |
| uint32_t | osEventFlagsSet (osEventFlagsId_t ef_id, uint32_t flags) |
| Set the specified Event Flags. More... | |
| uint32_t | osEventFlagsClear (osEventFlagsId_t ef_id, uint32_t flags) |
| Clear the specified Event Flags. More... | |
| uint32_t | osEventFlagsGet (osEventFlagsId_t ef_id) |
| Get the current Event Flags. More... | |
| uint32_t | osEventFlagsWait (osEventFlagsId_t ef_id, uint32_t flags, uint32_t options, uint32_t timeout) |
| Wait for one or more Event Flags to become signaled. More... | |
| osStatus_t | osEventFlagsDelete (osEventFlagsId_t ef_id) |
| Delete an Event Flags object. More... | |
| const char * | osEventFlagsGetName (osEventFlagsId_t ef_id) |
| Get name of an Event Flags object. More... | |
The event flags management functions in CMSIS-RTOS allow you to control or wait for event flags. Each signal has up to 31 event flags.
A thread
When a thread wakes up and resumes execution, its signal flags are automatically cleared (if event flags option osFlagsNoClear is not specified).
Here is a simple example that shows how two thread can communicate with each others using event flags:
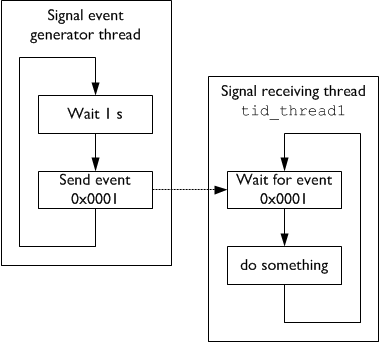
The following steps are required to use event flags:
The following complete example code can be directly used with the "CMSIS-RTOS2 main template" and is also provided as a stand-alone template for RTX5:
Code Example
| struct osEventFlagsAttr_t |
| Data Fields | ||
|---|---|---|
| const char * | name |
name of the event flags String with a human readable name of the event object. |
| uint32_t | attr_bits |
attribute bits No attributes available. |
| void * | cb_mem |
memory for control block Pointer to a memory location for the event object. This can optionally be used for custom memory management systems. Specify NULL to use the kernel memory management. |
| uint32_t | cb_size |
size of provided memory for control block The size of the memory block passed with cb_mem. Must be the size of an event object or larger. |
Event Flags ID identifies the event flags.
| osEventFlagsId_t osEventFlagsNew | ( | const osEventFlagsAttr_t * | attr | ) |
| [in] | attr | event flags attributes; NULL: default values. |
The function osEventFlagsNew creates a new event flags object that is used to send events across threads and returns the pointer to the event flags object identifier or NULL in case of an error.
The parameter attr sets the event flags attributes (refer to osEventFlagsAttr_t). Default attributes will be used if set to NULL.
Code Example
| uint32_t osEventFlagsSet | ( | osEventFlagsId_t | ef_id, |
| uint32_t | flags | ||
| ) |
| [in] | ef_id | event flags ID obtained by osEventFlagsNew. |
| [in] | flags | specifies the flags that shall be set. |
The function osEventFlagsSet sets the event flags specified by the parameter flags in an event flags object specified by parameter ef_id. All threads waiting for the flag set will be notified to resume from BLOCKED state. The function returns the event flags after setting or an error code if highest bit is set (refer to Flags Functions Error Codes).
| uint32_t osEventFlagsClear | ( | osEventFlagsId_t | ef_id, |
| uint32_t | flags | ||
| ) |
| [in] | ef_id | event flags ID obtained by osEventFlagsNew. |
| [in] | flags | specifies the flags that shall be cleared. |
The function osEventFlagsClear clears the event flags specified by the parameter flags in an event flags object specified by parameter ef_id. The function returns the event flags before clearing or an error code if highest bit is set (refer to Flags Functions Error Codes).
| uint32_t osEventFlagsGet | ( | osEventFlagsId_t | ef_id | ) |
| [in] | ef_id | event flags ID obtained by osEventFlagsNew. |
The function osEventFlagsGet returns the event flags currently set in an event flags object specified by parameter ef_id or 0 in case of an error.
| uint32_t osEventFlagsWait | ( | osEventFlagsId_t | ef_id, |
| uint32_t | flags, | ||
| uint32_t | options, | ||
| uint32_t | timeout | ||
| ) |
| [in] | ef_id | event flags ID obtained by osEventFlagsNew. |
| [in] | flags | specifies the flags to wait for. |
| [in] | options | specifies flags options (osFlagsXxxx). |
| [in] | timeout | Timeout Value or 0 in case of no time-out. |
The function osEventFlagsWait suspends the execution of the currently RUNNING thread until any or all event flags specified by the parameter flags in the event object specified by parameter ef_id are set. When these event flags are already set, the function returns instantly. Otherwise, the thread is put into the state BLOCKED. The function returns the event flags before clearing or an error code if highest bit is set (refer to Flags Functions Error Codes).
The options parameter specifies the wait condition:
| Option | |
|---|---|
| osFlagsWaitAny | Wait for any flag (default). |
| osFlagsWaitAll | Wait for all flags. |
| osFlagsNoClear | Do not clear flags which have been specified to wait for. |
If osFlagsNoClear is set in the options osEventFlagsClear can be used to clear flags manually.
The parameter timeout represents a number of timer ticks and is an upper bound. The exact time delay depends on the actual time elapsed since the last timer tick.
| osStatus_t osEventFlagsDelete | ( | osEventFlagsId_t | ef_id | ) |
| [in] | ef_id | event flags ID obtained by osEventFlagsNew. |
The function osEventFlagsDelete deletes the event flags object specified by parameter ef_id and releases the internal memory obtained for the event flags handling. After this call, the ef_id is no longer valid and cannot be used. This can cause starvation of threads that are waiting for flags of this event object. The ef_id may be created again using the function osEventFlagsNew.
Possible osStatus_t return values:
| const char * osEventFlagsGetName | ( | osEventFlagsId_t | ef_id | ) |
| [in] | ef_id | event flags ID obtained by osEventFlagsNew. |
The function osEventFlagsGetName returns the pointer to the name string of the event flags object identified by parameter ef_id or NULL in case of an error.
Code Example