 |
CMSIS-RTOS2
Version 2.1.0
Real-Time Operating System: API and RTX Reference Implementation
|
 |
CMSIS-RTOS2
Version 2.1.0
Real-Time Operating System: API and RTX Reference Implementation
|
Synchronize resource access using Mutual Exclusion (Mutex). More...
Data Structures | |
| struct | osMutexAttr_t |
| Attributes structure for mutex. More... | |
Macros | |
| #define | osMutexRecursive 0x00000001U |
| Mutex attributes (attr_bits in osMutexAttr_t). More... | |
| #define | osMutexPrioInherit 0x00000002U |
| Priority inherit protocol. More... | |
| #define | osMutexRobust 0x00000008U |
| Robust mutex. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef void * | osMutexId_t |
Functions | |
| osMutexId_t | osMutexNew (const osMutexAttr_t *attr) |
| Create and Initialize a Mutex object. More... | |
| const char * | osMutexGetName (osMutexId_t mutex_id) |
| Get name of a Mutex object. More... | |
| osStatus_t | osMutexAcquire (osMutexId_t mutex_id, uint32_t timeout) |
| Acquire a Mutex or timeout if it is locked. More... | |
| osStatus_t | osMutexRelease (osMutexId_t mutex_id) |
| Release a Mutex that was acquired by osMutexAcquire. More... | |
| osThreadId_t | osMutexGetOwner (osMutexId_t mutex_id) |
| Get Thread which owns a Mutex object. More... | |
| osStatus_t | osMutexDelete (osMutexId_t mutex_id) |
| Delete a Mutex object. More... | |
Mutual exclusion (widely known as Mutex) is used in various operating systems for resource management. Many resources in a microcontroller device can be used repeatedly, but only by one thread at a time (for example communication channels, memory, and files). Mutexes are used to protect access to a shared resource. A mutex is created and then passed between the threads (they can acquire and release the mutex).
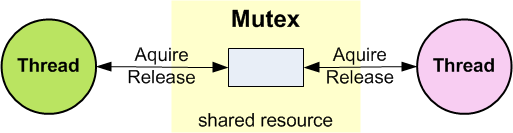
A mutex is a special version of a semaphore. Like the semaphore, it is a container for tokens. But instead of being able to have multiple tokens, a mutex can only carry one (representing the resource). Thus, a mutex token is binary and bounded. The advantage of a mutex is that it introduces thread ownership. When a thread acquires a mutex and becomes its owner, subsequent mutex acquires from that thread will succeed immediately without any latency (if osMutexRecursive is specified). Thus, mutex acquires/releases can be nested.
| struct osMutexAttr_t |
| Data Fields | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| const char * | name |
name of the mutex String with a human readable name of the mutex object. | ||||||||
| uint32_t | attr_bits |
attribute bits The following predefined bit masks can be assigned to set options for a mutex object.
| ||||||||
| void * | cb_mem |
memory for control block Pointer to a memory location for the mutex object. This can optionally be used for custom memory management systems. Specify NULL to use the kernel memory management. | ||||||||
| uint32_t | cb_size |
size of provided memory for control block The size of the memory block passed with cb_mem. Must be the size of a mutex object or larger. | ||||||||
| #define osMutexRecursive 0x00000001U |
Recursive mutex.
| #define osMutexPrioInherit 0x00000002U |
| #define osMutexRobust 0x00000008U |
Mutex ID identifies the mutex.
| osMutexId_t osMutexNew | ( | const osMutexAttr_t * | attr | ) |
| [in] | attr | mutex attributes; NULL: default values. |
The function osMutexNew creates and initializes a new mutex object and returns the pointer to the mutex object identifier or NULL in case of an error.
The parameter attr sets the mutex object attributes (refer to osMutexAttr_t). Default attributes will be used if set to NULL.
Code Example
| *const char * osMutexGetName | ( | osMutexId_t | mutex_id | ) |
| [in] | mutex_id | mutex ID obtained by osMutexNew. |
The function osMutexGetName returns the pointer to the name string of the mutex identified by parameter mutex_id or NULL in case of an error.
| osStatus_t osMutexAcquire | ( | osMutexId_t | mutex_id, |
| uint32_t | timeout | ||
| ) |
| [in] | mutex_id | mutex ID obtained by osMutexNew. |
| [in] | timeout | Timeout Value or 0 in case of no time-out. |
The blocking function osMutexAcquire waits until a mutex object specified by parameter mutex_id becomes available. If no other thread has obtained the mutex, the function instantly returns and blocks the mutex object.
The parameter timeout specifies how long the system waits to acquire the mutex. While the system waits, the thread that is calling this function is put into the BLOCKED state. The parameter timeout can have the following values:
Possible osStatus_t return values:
Code Example
| osStatus_t osMutexRelease | ( | osMutexId_t | mutex_id | ) |
| [in] | mutex_id | mutex ID obtained by osMutexNew. |
The function osMutexRelease releases a mutex specified by parameter mutex_id. Other threads that currently wait for this mutex will be put into the READY state.
Possible osStatus_t return values:
Code Example
| osThreadId_t osMutexGetOwner | ( | osMutexId_t | mutex_id | ) |
| [in] | mutex_id | mutex ID obtained by osMutexNew. |
The function osMutexGetOwner returns the thread object ID of the thread that acquired a mutex specified by parameter mutex_id. In case of an error or if the mutex is not owned by the thread, it returns NULL.
| osStatus_t osMutexDelete | ( | osMutexId_t | mutex_id | ) |
| [in] | mutex_id | mutex ID obtained by osMutexNew. |
The function osMutexDelete deletes a mutex object specified by parameter mutex_id. It releases internal memory obtained for mutex handling. After this call, the mutex_id is no longer valid and cannot be used. The mutex may be created again using the function osMutexNew.
Possible osStatus_t return values:
Code Example